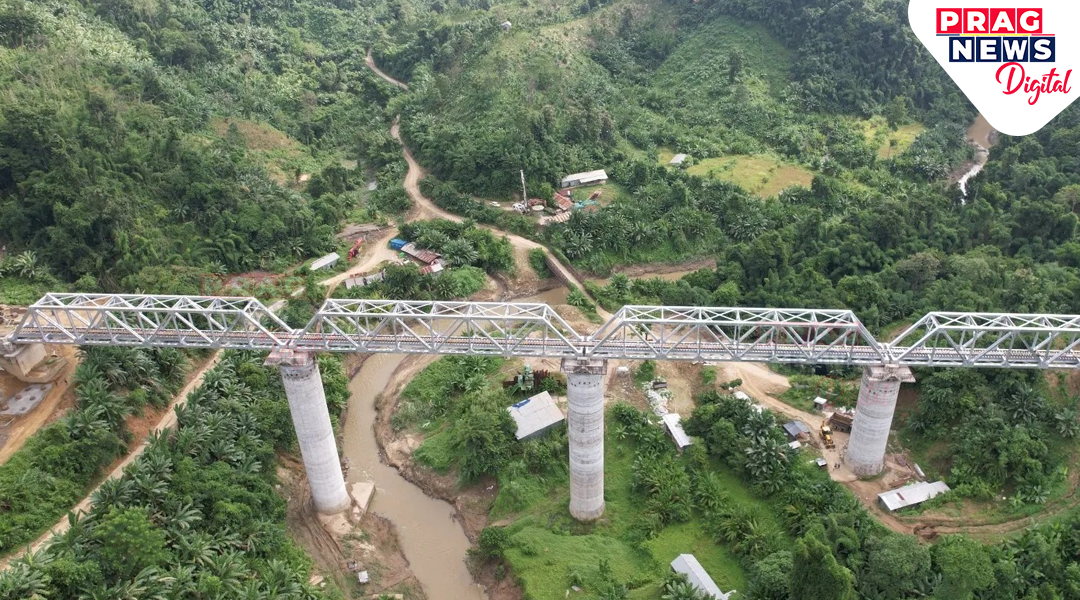
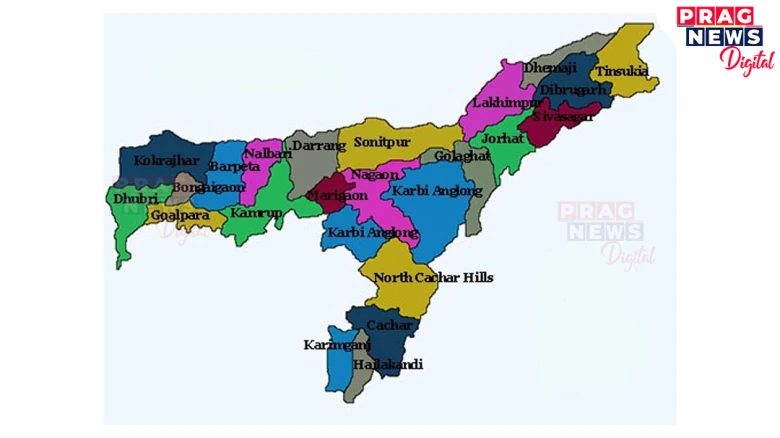
Assam is located between 24°8'N to 28°2'N latitude and 89°5'E to 96°1'E longitude. The state shares international borders with Bhutan and Bangladesh, while domestically it borders West Bengal, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, and Tripura.
Digital Desk: Assam, officially known as the State of Assam, is situated in Northeastern India and forms an integral part of the country’s northeastern region. The state covers an area of approximately 78,438 squarekilometres and is characterized by its diverse topography, including the Brahmaputra Valley, Barak Valley, and various hill ranges. The administrative structure of Assam comprises multiple districts, each serving specific administrative, developmental, and governance functions.
• Location and coordinates
Assam is located between 24°8'N to 28°2'N latitude and 89°5'E to 96°1'E longitude. The state shares international borders with Bhutan and Bangladesh, while domestically it borders West Bengal, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, and Tripura.
• Major Rivers and Topographical Features
The Brahmaputra River, one of Asia’s major rivers, flows through the heart of Assam, creating the fertile Brahmaputra Valley. The Barak River system dominates the southern regions, while numerous tributaries and smaller rivers create a complex hydrological network throughout the state.
ADMINISTRATIVE DISTRICTS OF ASSAM:
As of current administrative records, Assam consists of 35 districts, organized for effective governance, development implementation and administrative coordination. The districts are:
1. TINSUKIA
- Headquarters: Tinkusia
- Area: Approximately 3,790 square km
- Significance: Oil and coal mining region
2. DIBRUGARH
- Headquarters: Dibrugarh
- Area: Approximately 3,381 square km
- Significance: Tea Cultivation and Commercial Hub
3. SIBSAGAR
- Headquarters: Jorhat
- Area: Approximately2,668square km
- Significance: Historical Capital of Ahom Kingdom
4. JORHAT
- Headquarters: Jorhat
- Area: Approximately 2,851square km
- Significance: Tea research and cultural centre
5. GOLAGHAT
- Headquarters: Golaghat
- Area: Approximately 3,502square km
- Significance: Agricultural and Educational Centre
6. CHARAIDEO
- Headquarters: Sonari
- Area: Approximately 1,175square km
- Significance: Archaeological Importance
7. MAJULI
- Headquarters: Garamur
- Area: Approximately 880square km
- Significance: World’s largest river island
8. NAGAON
- Headquarters: Nagaon
- Area: Approximately 3,831square km
- Significance: Agricultural and Handloom centre
9. MORIGAON
- Headquarters: Morigaon
- Area: Approximately 1,704square km
- Significance: Agricultural Economy
10. HOJAI
- Headquarters: Hojai
- Area: Approximately 1,581square km
- Significance: Commercial and Transportation hub
11. WEST KARBI ANGLONG
- Headquarters: Hamren
- Area: Approximately 4,888square km
- Significance:Tribal autonomous region
12. KARBI ANGLONG
- Headquarters: Diphu
- Area: Approximately 6,431square km
- Significance: Largest district by area, Tribal region
13. DIMA HASAO
- Headquarters: Haflong
- Area: Approximately 4,888square km
- Significance: Hill district, tribal autonomous council
14. SONITPUR
- Headquarters: Tezpur
- Area: Approximately 5,324square km
- Significance: Tourism and Defence installations
15. BISWANATH
- Headquarters: Biswanath Chariali
- Area: Approximately 1,089square km
- Significance: Agricultural region
16. LAKHIMPUR
- Headquarters: North Lakhimpur
- Area: Approximately 2,277square km
- Significance: Agricultural and flood-prone region
17. DHEMAJI
- Headquarters: Dhemaji
- Area: Approximately 3,237square km
- Significance: Border district with Arunachal Pradesh
18. DARRANG
- Headquarters: Mangaldoi
- Area: Approximately 1,585square km
- Significance: Agricultural Economy
19. UDALGURI
- Headquarters: Udalgiri
- Area: Approximately 1,852square km
- Significance: Tribal and agricultural region
20. KAMRUP
- Headquarters: Amingaon
- Area: Approximately 4,345square km
- Significance: Rural areas around state capital
21. KAMRUP METROPOLITAN
- Headquarters: Guwahati
- Area: Approximately 1,530square km
- Significance: State capital and commercial centre
22. NALBARI
- Headquarters: Nalbari
- Area: Approximately 2,257square km
- Significance: Agricultural and handloom region
23. BARPETA
- Headquarters: Barpeta
- Area: Approximately 3,245square km
- Significance:Culturan and Religious significance
24. BAJALI
- Headquarters: Pathsala
- Area: Approximately1,196square km
- Significance: Agriculture region
25. BAKSA
- Headquarters: Mushalpur
- Area: Approximately 2,400square km
- Significance: Bodo tribal autonomous region
26. CHIRANG
- Headquarters: Kajalgaon
- Area: Approximately 1,923square km
- Significance: Bodo territorial region
27. KOKRAJHAR
- Headquarters: Kokrajhar
- Area: Approximately 3,169square km
- Significance: Bodo Autonomous council headquarters
28. CACHAR
- Headquarters: Silchar
- Area: Approximately 3,786 square km
- Significance: Commercial hub of Brak Valley
29. HAILAKANDI
- Headquarters: Hailakandi
- Area: Approximately 1,327square km
- Significance: Agricultural and border district
30. KARIMGANJ
- Headquarters: Karimganj
- Area: Approximately 1,809square km
- Significance: International border district
31. TAMULPUR
- Headquarters: Tamulpur
- Area: Approximately 1,781square km
- Significance: Newly formed district
32. BONGAIGAON
- Headquarters: Bongaigaon
- Area: Approximately 1,724square km
- Significance: Industrial and petrochemical hub
33. GOALPARA
- Headquarters: Goalpara
- Area: Approximately 1,824square km
- Significance: Historical and Cultural significance
34. SOUTH SALMARA-MANKACHAR
- Headquarters: Mankachar
- Area: Approximately 568square km
- Significance: International border district
35. DHUBRI
- Headquarters: Dhubri
- Area: Approximately 2,838square km
- Significance: River port and trade centre
• Districts Administration
Each district is administered by a District Collector or Deputy Commissioner, who serves as the chief administrative officer. The districts are further subdivided into:
- Sub-Divisions
- Development Blocks
- Revenue circles
- Villages and town areas
• Autonomous Councils
Several districts fall under autonomous council administration:
- Bodoland Territorial Council (BTC) covering Kokrajhar, Chirang, Baksa, and Udalguri
- Karbi Anglong Autonomous Council
- Dima Hasao Autonomous Council
• Recent administrative Changes
Notable recent additions include:
- Charaideo (2015)
- Hojai (2015)
- West Karbi Anglong (2016)
- Biswanath (2015)
- Bajali (2020)
- Tamulpur (2020)
• Border Districts
Several districts share international borders, making them strategically important:
- Dhubri, South Salmara-Mankachar, Karimganj (Bangladesh border)
- Kokrajhar, Chirang, Baksa, Udalguri (Bhutan border)
The administrative geography of Assam reflects a complex interplay of historical evolution, cultural diversity and developments needs. The current districts, represents efforts to balance administrative efficiency with local governance requirements. Future administrative planning must consider demographic changes, urban growth patterns, and unique requirements of tribal and border areas to ensure sustainable developments across all districts of Assam.